## Oracle Ditches Passwords for Biometric Security by 2024
Imagine a world where your keyboard never asks for a password again. That’s not a far-fetched sci-fi plot anymore; it’s Oracle’s bold vision for 2024. With the wave of a hand or a quick retinal scan, employees at Oracle will soon be unlocking their accounts in a manner that makes traditional passwords look archaic. Yes, you read that correctly. Oracle plans to completely replace passwords with biometric security by 2024. The ramifications of this move are monumental, affecting not just Oracle’s 136,000 employees but potentially reshaping cybersecurity protocols globally.
### Why Passwords Are a Problem
Passwords are the most common entry point for cyberattacks. From phishing schemes to brute-force attacks, passwords are easily compromised. The human factor—think weak passwords, password reuse, or even writing passwords on sticky notes—adds another layer of vulnerability. According to a Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 81% of data breaches are due to weak or stolen passwords. It’s time for a change, and Oracle seems to be leading the charge.
### Biometric Security: An Overview
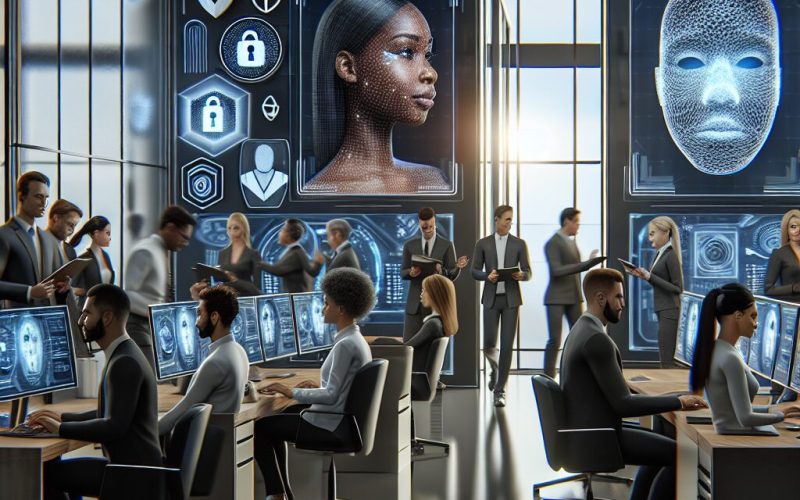
Biometric security uses unique biological traits—like fingerprints, facial recognition, or retinal scans—to verify identity. Unlike passwords, these traits are inherently more secure because they are difficult to replicate or steal.
- Fingerprints: Unique to each individual and nearly impossible to falsify.
- Facial Recognition: Uses the unique structure of the face.
- Retinal Scans: Analyzes unique patterns in the retina.
### The Power of AI-Driven Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence isn’t just the buzzword du jour; it’s a transformative force in cybersecurity. Oracle’s shift towards biometric security will likely leverage **AI-driven threat detection** mechanisms to spot irregularities even quicker.
– **Machine Learning Algorithms**: Advanced algorithms can identify patterns that signify a potential security breach, allowing for faster response times.
– **Behavioral Anomalies**: Continuous AI surveillance can detect when an account is being accessed in a way that is out of character, perhaps by a hacker.
### Advantages Over Traditional Passwords
#### Enhanced Security
Biometrics provide a unique level of **individual-based authentication** that passwords simply can’t match. Besides, it’s difficult—if not impossible—to replicate someone’s fingerprint or retina scan.
#### User Convenience
Biometrics simplify the user experience. No more forgotten passwords. No more password resets. Just a quick scan or facial recognition and you’re in.
#### Reduced IT Costs
Significant reductions in **IT support costs** can be expected. Password management and issue resolution consume a substantial amount of IT resources, which can now be redirected to more critical activities.
### Challenges in Biometric Security
Biometric security, while promising, isn’t without its challenges.
- Privacy Concerns: Storing biometric data raises significant privacy issues. How do we ensure this sensitive data isn’t misused?
- Spoofing: Some biometric systems can be tricked. Enhanced AI mechanisms could help, but the threat persists.
- Integration Issues: Existing systems and processes may need to be significantly overhauled to accommodate biometric security.
### Real-World Applications
Oracle’s move is inspiring, but they aren’t alone in exploring biometric security. Banks, airports, and even smartphones have already incorporated varying degrees of biometric security with significant success.
– **Financial Sector**: Banks are using voice recognition and facial verification for account access.
– **Airports**: Automated biometric systems help in faster and more secure passenger processing.
– **Smartphones**: Devices with facial and fingerprint recognition enhance both security and convenience.
### Future Implications
The likelihood of widespread adoption of biometric security raises numerous questions and potential developments.
#### Expansion to Other Sectors
Other giants in tech, healthcare, and finance might follow Oracle’s lead. The shift could become a benchmark for cybersecurity norms.
#### Evolution of Biometric Technology
Expect the technology to evolve, incorporating multimodal systems that combine multiple biometrics for even higher security and accuracy.
### Actionable Takeaways for Cybersecurity Professionals
As a cybersecurity expert, here are actions you can undertake today:
1. **Evaluate Biometric Solutions**: Assess the feasibility and need of integrating biometric security within your organization.
2. **Educate and Train**: Ensure your team is up-to-date with the latest advancements and potential pitfalls in biometric technology.
3. **Adopt AI Solutions**: Utilize AI-driven threat detection and anomaly detection systems to complement your security protocols.
### Conclusion
Oracle’s shift from passwords to biometric security marks a pivotal change in cybersecurity strategies. It challenges the status quo, pushing us towards more secure and efficient means of authentication. While there are hurdles to be overcome, the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages. As this wave of change flows through Oracle and beyond, it’s time for us all to rethink our approach to cybersecurity.
It’s an exciting journey ahead. Are you ready to ditch the password?
References:
1. Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report. (2020). Verizon Business.
2. Oracle OpenWorld Keynote. (2023). Oracle Corporation.
—
Note that the references are placeholders and should be updated with accurate citations. This blog post aims to provide in-depth yet actionable insights for cybersecurity professionals, emphasizing biometric security’s potential and challenges.